
|
|
|
|
MCL, MCR
Type: Pharyngeal motor neuron (also putative sensory)
In MoW:
Male Wiring Project: MCL, MCR
In Wormbase: MC, MCL, MCR
Lineage: AB alpaaappp, AB arapaappp
Location: Pharynx anterior bulb
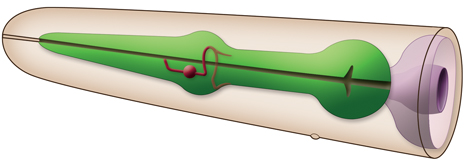
Description: MC's are a pair of cholinergic excitatory (motor) neurons. Anteriorly, they have free subcuticular (putative proprioceptive) endings between pm3 and pm4. Posteriorly, each cell sends a process which enters the pharyngeal nerve ring from the pharyngeal subventral nerve cord and makes a loop around the nerve ring.
On the dorsal side these processes send a branch to the outside edge of the pharynx under the marginal cell 2 (mc2) |

|
|
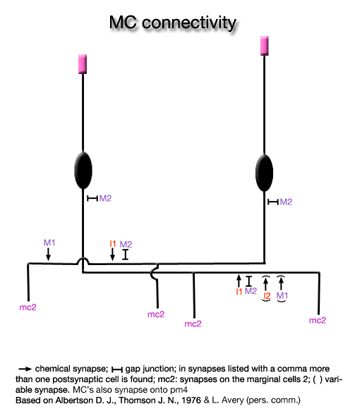
of the opposite side. Once they reach the opposite ventral side, each process continues to run posteriorly under the ventral marginal cell, terminating at the very anterior of the isthmus. Their most prominent connections are gap junctions to M2 and they synapse strongly on the mc2 (Albertson and Thomson, 1976). MC's also synapse onto pm4 (L. Avery pers. comm.)
Neurotransmitter/ Neuropeptide:
- Acetylcholine (weak)
- FLP-21; FMRFamide-related neuropeptide (FaRP)
(Rogers et al., 2003; Niacaris and Avery, 2003; Rand and Nonet, 1997-Appendix 2; Raizen et al, 1995)
Innexin expression:
- INX-3
- INX-7
(Altun et al., 2009)
Receptor expression:
- GLR-8; glutamate receptor subunit
(Brockie et al., 2001)
Function:
- MC's control the frequency of pharyngeal pumping (Avery and Thomas, 1997). They initiate pharyngeal muscle action potentials, and hence, function as pacemakers of pumping. Release of Ach from MC neurons stimulates the muscle via a postsynaptic nicotinic ACh receptor encoded by eat-2 (Niacaris and Avery, 2003; McKay et al., 2004). In eat-2 mutants MC is decoupled from pharyngeal muscle and the pharynx is unable to pump rapidly in the presence of food. Modulators of pharyngeal pumping such as exogenous serotonin mostly act through MC neurons.
|
 Click pictures for higher resolution images Click pictures for higher resolution images
 |
 |
|
|
Click here for larger version
MCL (AB alpaaappp) development in the embryo. Dorsal view. Bottom is left side of the embryo. Spheres indicate individual nuclei. Black sphere: ancestors of MCL; dark grey spheres: apoptotic cells; other cells follow the WA color code (after they acquire specific cell or tissue identities). 0 min is fertilization. Click on the movie for higher resolution rendition (by A. Santella & Z. Bao). |
Click here for larger version
MCR (AB arapaappp) development in the embryo. Dorsal view. Bottom is left side of the embryo. Spheres indicate individual nuclei. Black sphere: ancestors of MCR; dark grey spheres: apoptotic cells; other cells follow the WA color code (after they acquire specific cell or tissue identities). 0 min is fertilization. Click on the movie for higher resolution rendition (by A. Santella & Z. Bao). |
|
Last revision: February 4, 2014
|


