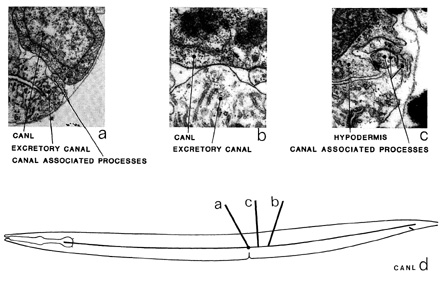
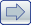
CAN is a set of two cells that are closely associated with the excretory canal. The cell bodies
of CAN are situated adjacent and dorsal to the excretory canal at about the level of the vulva
(d). Anteriorly and posteriorly directed processes emanate from the cell bodies and run along
the canal in close association with the processes of ALA and PVD. The anterior process of CAN ends just behind the nerve ring (d). The three canal-associated processes on each side, ALA, CAN and PVD, have not been completely reconstructed although they have been sampled in
several places. Two of the processes end at about the level of the anus and the third enters the
pre-anal ganglia and synapses onto PVC (ALA-d). A single synapse onto the lateral
hypodermis has also been seen on one of the processes (c). Apart from a few rather
unconvincing gap junctions to the excretory canal (b), no other synapses can be unambiguously
assigned to CAN. Laser ablation experiments have, however, shown it to be essential for the
survival of the animal (J. Sulston, unpublished observations).
Magnifications: (a) x 12750, (b, c) x 25500.
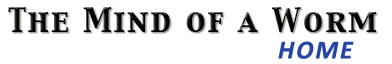
Click pictures for higher resolution images