|
VB1, VB2, VB3, VB4, VB5, VB6, VB7, VB8, VB9, VB10, VB11
Type: Motor neuron, sensory neuron (proprioceptive)
In MoW: VBn
Male Wiring Project: VBn, VB05, VB06, VB07, VB08, VB09, VB10, VB11
In Wormbase: VB1, VB2, VB3, VB4, VB5,
VB6, VB7, VB8, VB9, VB10, VB11
Lineage: P1.aaap, W.aap, P2.aaap, P3.aaap,
P4.aaap,
P5.aaap, P6.aaap, P7.aaap, P8.aaap,
P9.aaap,
P10.aaap, P11.aaap
Location: Body (ventral nerve cord)
Description: Postembryonically born. Ventral cord motor neurons. The connectivity of VB1, VB4 and VB7 differ slightly from the remaining VBs (Haspel & Donovan 2011)
Neurotransmitter/ Neuropeptide:
- Acetylcholine
(Loer, 2010; Duerr et al, 2008; Rand and Nonet, 1997-Appendix 2)
Innexin expression:
- INX-3
- INX-12
- UNC-9
(Altun et al., 2009)
Receptor expression:
|



|
Function:
- Locomotion
- Proprioception involving propagation of rhythmic activities along the body during forward locomotion; ventral and dorsal bending of an anterior body region directly activates VB and DB motor neurons (Wen et al., 2012). Gap junctions between neighbors as well as overlapping segments of their processes then propagate the bending signal from anterior to posterior. The mechanosensitive-proprioceptive receptors are likely localized near the anterior of the processes |
|
 Click pictures for higher resolution images Click pictures for higher resolution images
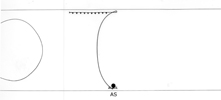
Schematic diagrams of
the ventral cord motor neurons
AS Neurons
 |
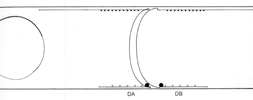
DA and DB Neurons
 |
VA Neurons

|
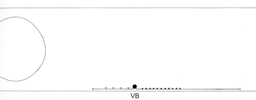
VB Neurons
 |
VC Neurons
 |
DD and VD Neurons
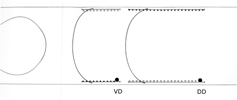 |
In all diagrams,axon processes with
neuromuscular synapses (NMJ) are shown as  whereas dendritic processes where synaptic inputs are received are shown as whereas dendritic processes where synaptic inputs are received are shown as  . .
Class A axons run forward in both
cords (VNC and DC) whereas the class B axons run backwards. The dendritic branches
of the dorsal and ventral class A neurons run in opposite directions as do those
from class Bneurons. Ventral class D neurons receive their synaptic input on
the dorsal side and give NMJ's on the ventral side. The dorsal type D neurons
have half the periodicity of their ventral counterparts and receive synapses
on the ventral side and give NMJ's on the dorsal side. Class AS neurons only
synapse on the dorsal side and have no ventral counterpart, whereas, the class
C neurons only synapse on the ventral side. The synapses from class C motor
neurons onto body muscles are less dense than for the other classes (White
J. et al, 1976.)
Synaptic map and process positioning of the ventral cord motor neurons
Connections of each motor neuron class
| Motor neuron class |
Chemical synapses to other motor neurons |
Chemical synapses from |
Gap junctions |
| AS |
DA, DD, VD |
AVA, AVB, AVD, AVE |
DA, VA, AVA |
| DA |
DB, DD, VD |
AVA, AVD, AVE, HSNR, PVCL, SABVL |
AS, VA, AVA |
| DB |
AS, DD, VD |
DVA, PVC, PVR |
DB, VB, AVB |
| DD |
VD |
RID, VC1-3 |
DD, VD |
| VA* |
DD, VA, VB, VD |
AVA, AVB, AVD, AVE |
AS, DA, AVA, SABD |
| VB* |
DD, VA, VD |
PVC |
VB, DB, AVB |
| VD |
VA, VB |
AVEL, PVNR, VC1-3 |
DD, VA, VD, PVPR |
| (Based on the Mind of a Worm and Haspel & Donovan 2011; *VA1,3,5 and VB1,4,7 have slightly different connections than the remainder of the class) |
|

 Click pictures for higher resolution images
Click pictures for higher resolution images