|
DD1, DD2, DD3, DD4, DD5, DD6
Type: Motor neuron
In MoW: DDn
Male Wiring Project:
DD01,
DD02,
DD03,
DD04,
DD05,
DD06
In Wormbase: DDn, DD1, DD2, DD3, DD4, DD5,
DD6
Lineage: AB plppappap, AB prppappap
AB plppapppa, AB prppapppa
AB plppapppp, AB prppapppp
Location: Body (ventral nerve cord)
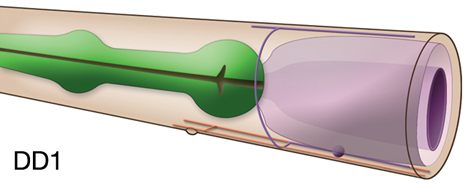
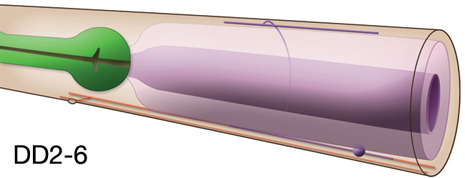
Description: GABAergic inhibitory ventral cord motor neurons. DD's receive dyadic synapses from excitatory ventral cord motor neurons along with body wall muscles. The initial pattern of synapses made by DD neurons are presynaptic and inhibitory to ventral body wall muscles while being postsynaptic to neurons that activate dorsal body wall muscles. During late L1, after the birth of VD motor neurons, DD neurons change their |
|
synaptic pattern such that their dorsal branches become presynaptic and inhibitory to dorsal body wall muscles while their ventral branches become postsynaptic to excitatory neurons that synapse on ventral body wall muscles (White et al., 1978; Walthall et al., 1993). Hermaphrodites and males exhibit some differences in DDn connectivity.
Neurotransmitter/ Neuropeptide:
- GABA
(Rand and Nonet, 1997-Appendix 2)
Innexin expression:
- INX-3
- INX-10
- INX-14
- UNC-7
- UNC-9
(Altun et al., 2009)
Receptor expression:
- ACR-14; nicotinic AChR non-alpha subunit
(Fox et al., 2005)
Function:
- Sinusoidal body movement-locomotion. DD's receive input from VA and VB neurons, and hence, are likely to be active during ventral muscle contractions. They form neuromuscular junctions dorsally that coordinately relax the dorsal muscles during ventral muscle contraction (Driscoll and Kaplan, 1997). D-type neurons may also regulate the wave amplitude of the sinusoidal movement since unc-25 and unc-30 mutants that lack functional D neurons generate rhythmic sinusoidal movement with a reduced amplitude (McIntire et al., 1993). |
 Click pictures for higher resolution images Click pictures for higher resolution images
| |
 |
|
Male Wiring Project
Note: In males, the DD6 cell body lies posterior to the male-specific CP9 neuron, which defines the anterior boundary of the male pre-anal ganglion (see Male Tail Cell ID). In males, DD6 is therefore considered part of the pre-anal ganglion rather than the ventral nerve cord.
For Male Wiring Project details see Emmons lab website.
Schematic Diagrams of
Ventral Cord motor neurons:
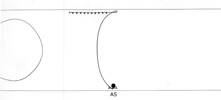
AS Neurons
 |
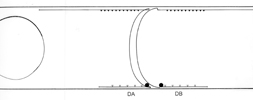
DA and DB Neurons
 |
VA Neurons

|
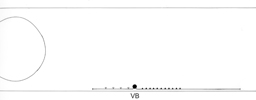
VB Neurons
 |
VC Neurons
 |
DD and VD Neurons
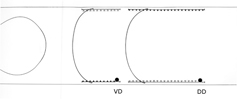 |
In all diagrams,axon processes with
neuromuscular synapses (NMJ) are shown as  whereas dendritic processes where synaptic inputs are received are shown as whereas dendritic processes where synaptic inputs are received are shown as 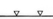 . .
Class A axons run forward in both
cords (VNC and DC) whereas the class B axons run backwards. The dendritic branches
of the dorsal and ventral class A neurons run in opposite directions as do those
from class Bneurons. Ventral class D neurons receive their synaptic input on
the dorsal side and give NMJ's on the ventral side. The dorsal type D neurons
have half the periodicity of their ventral counterparts and receive synapses
on the ventral side and give NMJ's on the dorsal side. Class AS neurons only
synapse on the dorsal side and have no ventral counterpart, whereas, the class
C neurons only synapse on the ventral side. The synapses from class C motor
neurons onto body muscles are less dense than for the other classes (White
J. et al, 1976.)
Synaptic map and process positioning of the VNC motor neurons (from White
J. et al, 1976):
Connections of each motor neuron class
| Motor neuron class |
Chemical synapses to other motor neurons |
Chemical synapses from |
Gap junctions |
| AS |
DA, DD, VD |
AVA, AVB, AVD, AVE |
DA, VA, AVA |
| DA |
DB, DD, VD |
AVA, AVD, AVE, HSNR, PVCL, SABVL |
AS, VA, AVA |
| DB |
AS, DD, VD |
DVA, PVC, PVR |
DB, VB, AVB |
| DD |
VD |
RID, VC1-3 |
DD, VD |
| VA* |
DD, VA, VB, VD |
AVA, AVB, AVD, AVE |
AS, DA, AVA, SABD |
| VB* |
DD, VA, VD |
PVC |
VB, DB, AVB |
| VD |
VA, VB |
AVEL, PVNR, VC1-3 |
DD, VA, VD, PVPR |
| (Based on the Mind of a Worm and Haspel & Donovan 2011; *VA1,3,5 and VB1,4,7 have slightly different connections than the remainder of the class) |
|